Table of Contents
Introduction
Past perfect verbs are used to talk about actions that happened before a point of time or an action in the past.
The reference to the past should show the order of the two actions. The action that happened first is in the past perfect, while the action that happened later (closer to the present) is in the past simple.
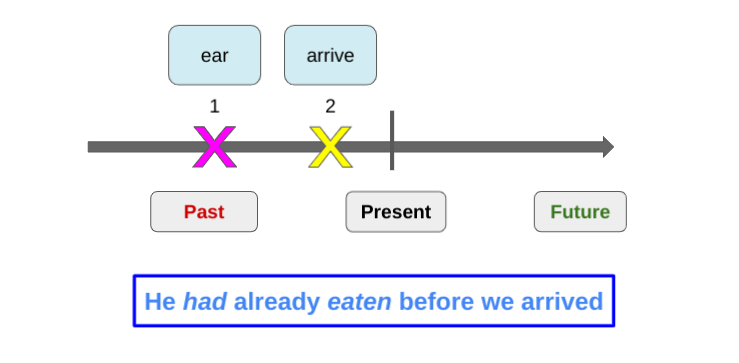
Examples:
- She had written two books before she signed up for the competition.
- They had visited several places by the time we spoke to them.
- He had cleaned up the area when the police arrived.
Forms
In the past perfect tense, the auxiliary had and the past participle of the verb are used in all forms and with all subjects (I, we, you, they, he, she, it).Affirmative Sentences:
Subject + had + past participle
- She couldn’t sleep because she had eaten a heavy meal.
- I went to bed after I had completed reviewing my notes.
- By the time we arrived at the bus station, the bus had left.
Negative Sentences
Subject + had + not + past participle
- I hadn’t seen her CV before I interviewed her.
- They refused to meet us because we hadn’t sent a confirmation email.
- She hadn’t eaten anything when the class started.
Questions
(Wh-) Had + subject + past participle?
- Had she completed the assignment before the deadline?
- What had they done to deserve that punishment?
- Had you learned Spanish before you went to Spain?
Signal words used with the past perfect
The following signal words are used with the past perfect tense:
by the time / when / before / after / already / just / never / yet
Examples:
- By the time the firefighters arrived, the neighbors had extinguished the fire.
- When the guests arrived, my mother had finished cooking.
- Before Emma left to Italy, she had taken a course in the Italian language.
- They took a final decision after they had discussed all the details.
- I didn’t eat in the party because I had already eaten.
- He had just arrived home when he received his manager’s message.
- I had never thought of learning Japanese before I watched that movie.
- The children had not slept yet when we arrived home.
Note:
The signal words used with the past perfect are the same as those used with the present perfect, but those used with the past perfect refer to the past.