Table of Contents
Introduction
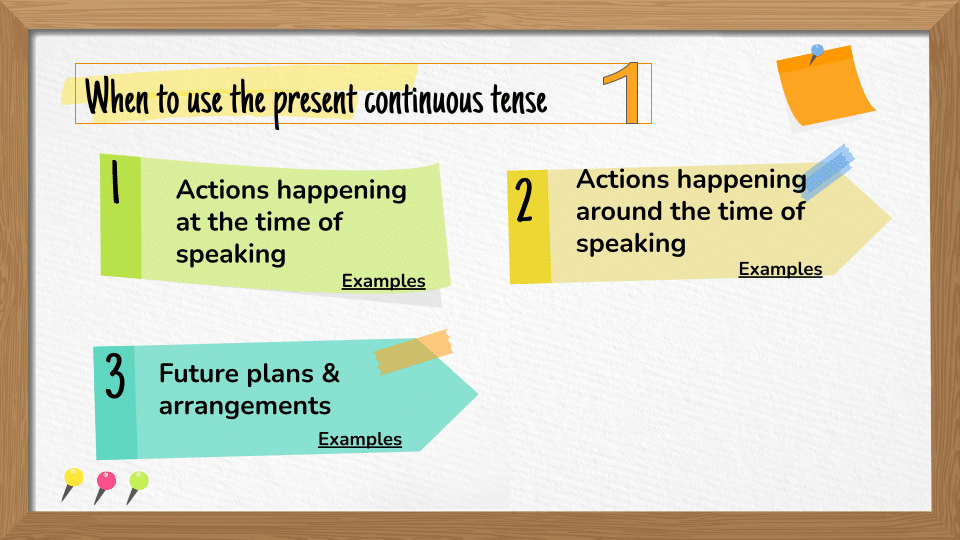
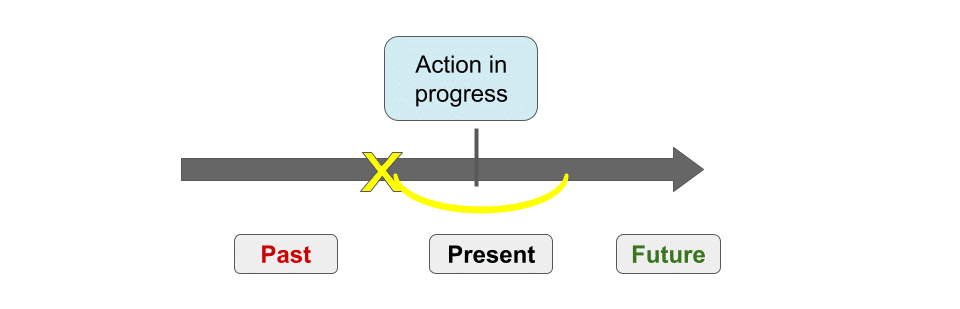
Present Continuous (or Progressive) Tense describes an action in progress at the time of speaking (e.g. now) or around the time of speaking (e.g. this term). The action started sometime in the past, is in progress now, and may continue for sometime n the future.
Forms
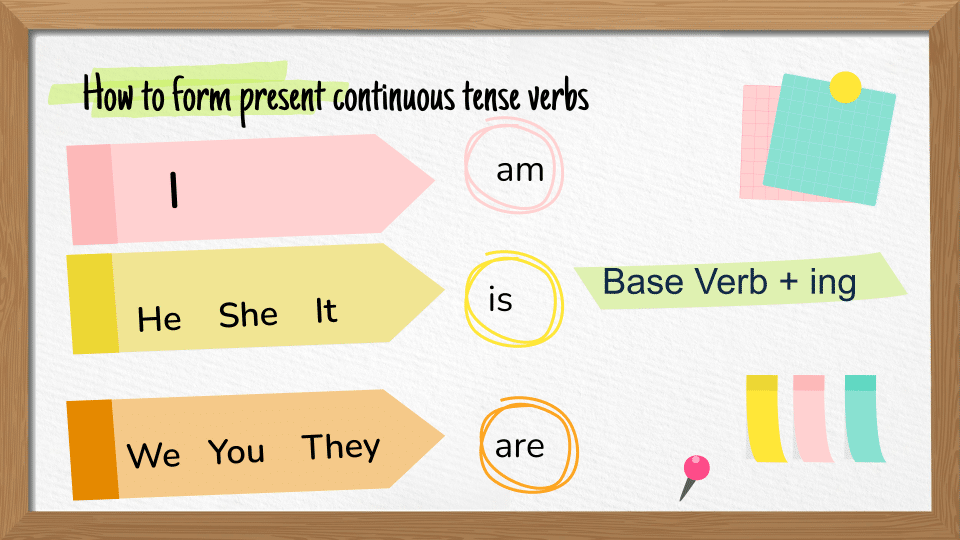
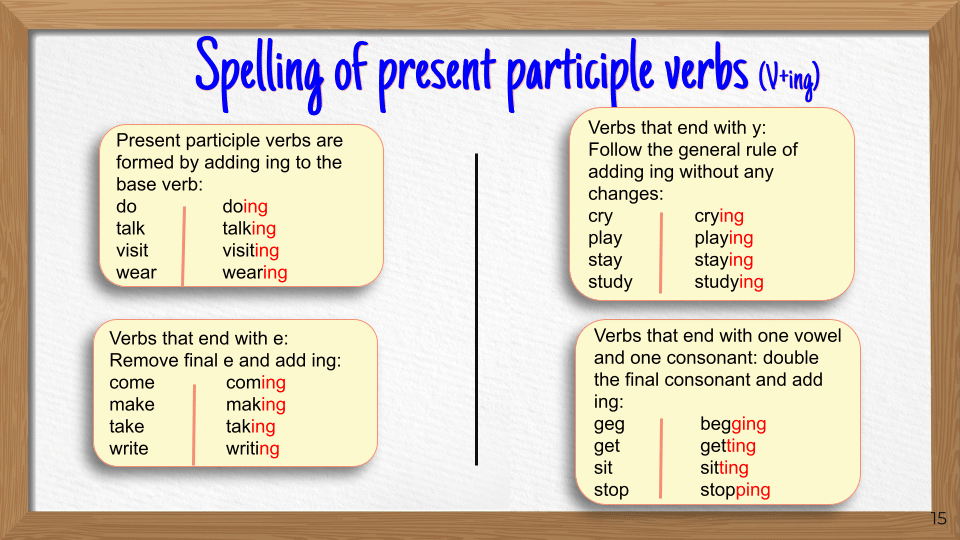
Affirmative sentences
| Subject | Verb Be | Base Verb + ing |
|---|---|---|
| I | am | Base Verb + ing |
| She, He, It | is | Base Verb + ing |
| We, You, They | are | Base Verb + ing |
Examples:
- We are watching a football match now.
- I am cooking for the guests right now.
- My little daughter is sleeping at the moment.
- They are helping us paint the walls.
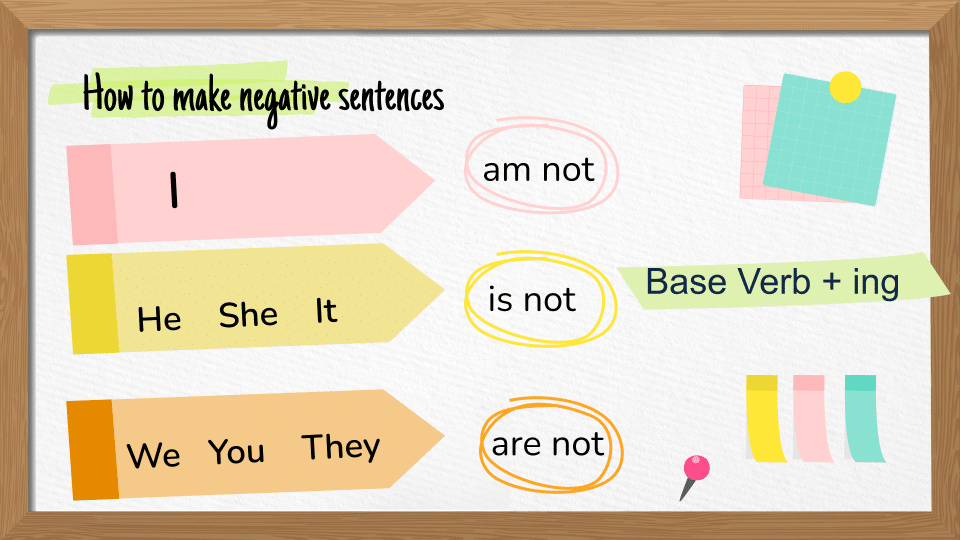
Negative sentences
| Subject | Verb Be | Base Verb + ing |
|---|---|---|
| I | am not | Base Verb + ing |
| She, He, It | is not | Base Verb + ing |
| We, You, They | are not | Base Verb + ing |
Examples:
- I am not taking any courses these days.
- My father isn’t waiting for us now.
- You are not telling the truth.
- The children aren’t listening to the teacher.
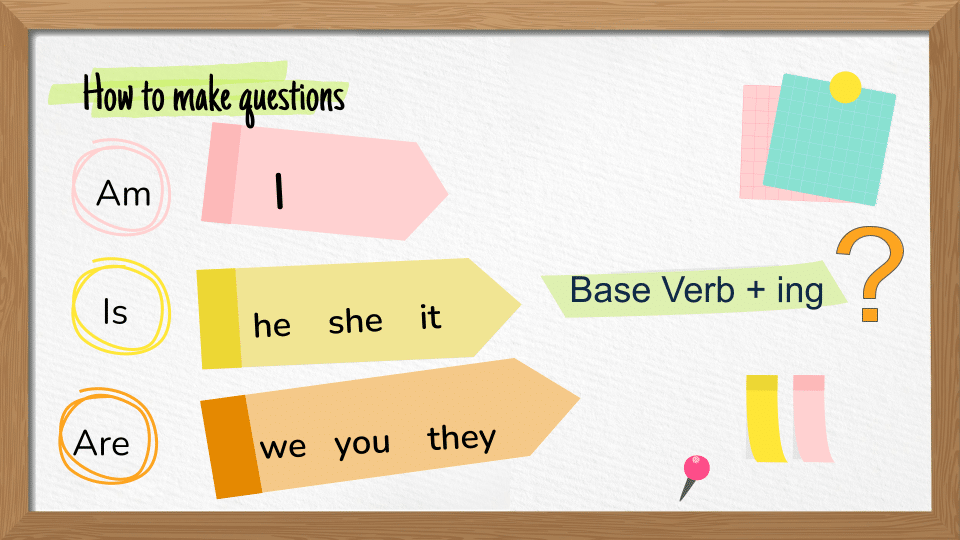
Questions
| Verb Be | Subject | Base Verb + ing |
|---|---|---|
| (Wh) Am | I | Base Verb + ing |
| (Wh) Is | she, he, it | Base Verb + ing |
| (Wh) Are | we, you, they | Base Verb + ing |
Examples:
- Am I talking too fast?
- Is the baby sleeping now?
- Are you still living in London?
- What are they doing right now?
- When is she coming back?
Other uses of the present continuous
In addition to actions happening at the time of speaking or around the time of speaking, present continuous verbs can be used to describe future actions, repeated actions, and developing actions.
Future actions
The present continuous can express planned near future actions. Future time markers are used to indicate the time.
Examples:
- I’m visiting the dentist tomorrow.
- He is moving to a new apartment next month.
- They are arriving in the evening.
- We are holding a meeting in two days.
To find out other ways to express future actions check the future simple tense.
Repeated actions
We usually use the present simple tense to talk about repeated actions, but when we want to imply that we are irritated or annoyed by the action, we use the present continuous.
The adverb of frequency always is usually used in these sentences.
- He is always complaining about his boss.
- She is always losing her car keys.
- The children are always making noise while I’m talking on the phone.
Changing, growing or developing actions
- Petrol prices are increasing these days.
- Your hair is growing very fast!
- More and more people are shopping online nowadays.
- She is visiting a lot of social media websites these days.
Time markers
These words/phrases are used to indicate the time of present continuous verbs.
- now
- right now
- at the moment
- at present
- at the present time
- presently
- currently
- for the time being
- these days
- nowadays
- today, this month, this year, etc.
In addition, expressions that draw the attention of the listener are indicators of actions happening now. These include: look, listen, Be careful, etc.
Examples:
- Look! The boy is throwing stones.
- Listen! Somebody is asking for help.
- Keep quiet! Your sister is studying now.
- Shshsh! The baby is sleeping.
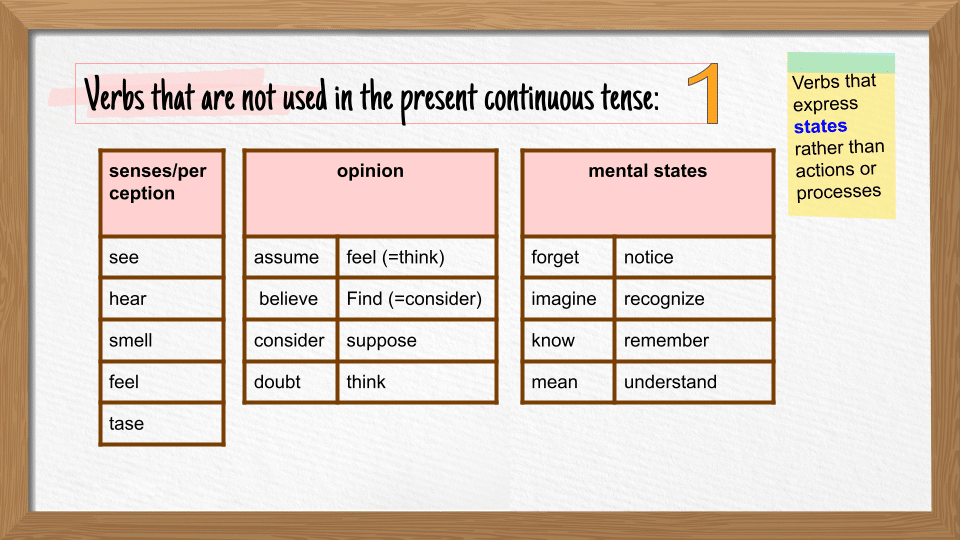
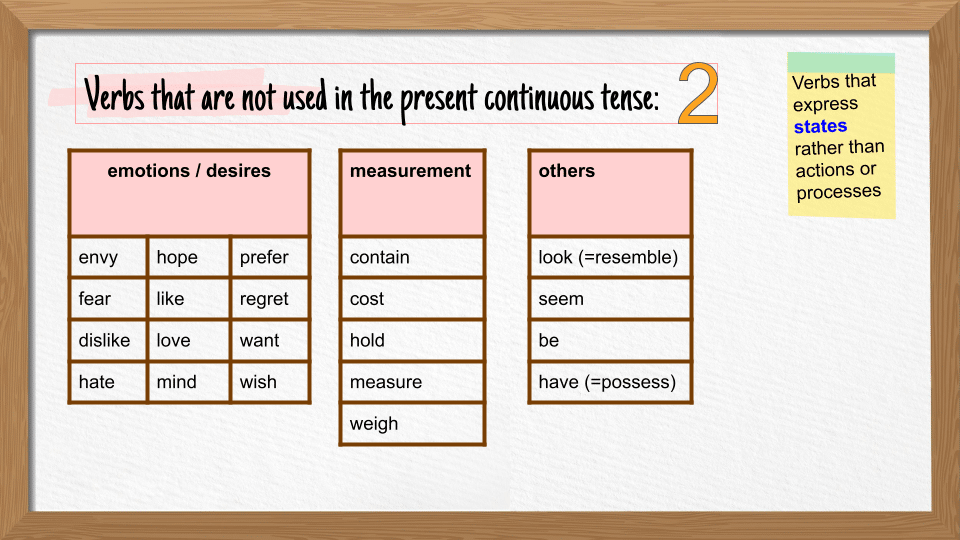
Verbs that cannot be used in continuous tenses
A group of verbs that describe the state of the subject are always used in simple tenses. They are not used in continuous tenses because this tense has a duration (beginning, progress and end), which does not apply to the state verbs.
For a complete list of the state verbs and examples, check Stative Verbs.
Examples:
- I like reading about the behavior of ants.
- The worker seems tired after working for 8 long hours.
- My book contains plenty of exercises.
- This perfume smells great.
Some of these verbs can be used as both stative verbs and action verbs but with different meanings.
- The flower smells nice. (state verb describing the smell of the flower)
Compare with:
- The girl is smelling the flower. (action verb describing what the girl is doing)
For more details, check Stative Verbs.
⇔ Take a quiz on present continuous tense.
⇔ Take a quiz on present continuous vs. present simple tense.