Table of Contents
What are comparative adjectives?
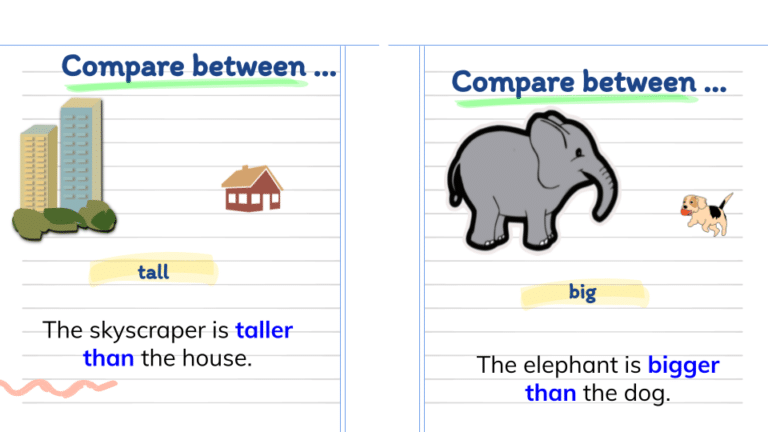
They are one form of adjectives used to compare two people, things, places, etc. Typically, we add er to the adjective and we connect the two items compared with than.
- A giraffe is taller than a horse.
- Rita is smarter than her friend.
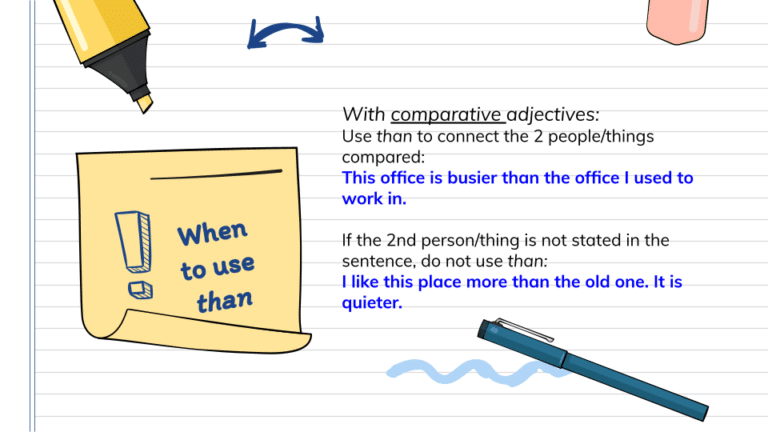
If the second person, thing, etc is understood from the context, we do not use than.
- This building is tall, but that one is taller.
What are superlative adjectives?
They are one form of adjectives used to compare one person, thing, place, etc. with the whole group they belong to. Typically, we add est to the adjective and we use the before the adjective.
- Giraffes are the tallest animals.
- Rita us the smartest girl in her class.
We use in or of to specify the group we are comparing with. However, if the group is understood from the context, we do not need to use in / of.
- Travelling by bus is cheaper than travelling by car, but the train is the cheapest.
To make the comparative and superlative adjectives, we follow certain rules, taking into account the number of syllables in the simple adjective.
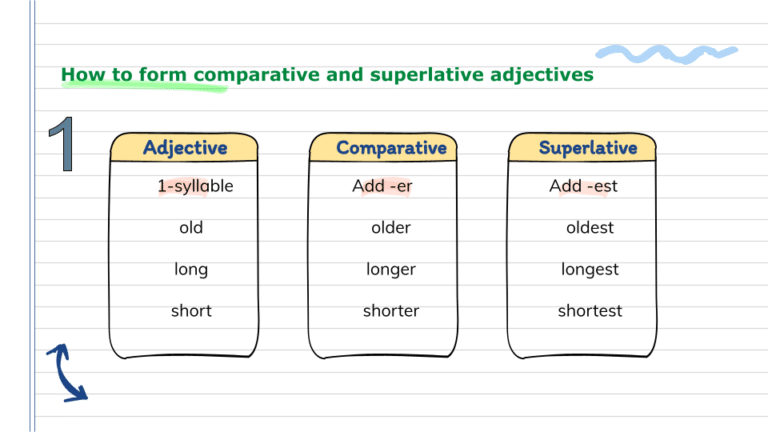
One-syllable adjectives
Comparative: simple adjective + er + than
The word than is used to connect the two items we are comparing.
- She is smarter than her sister.
- My father is older than your father.
Superlative: the + simple adjective + est + in / of
- She is the smartest student in her class.
- Sayed is the oldest player in the team.
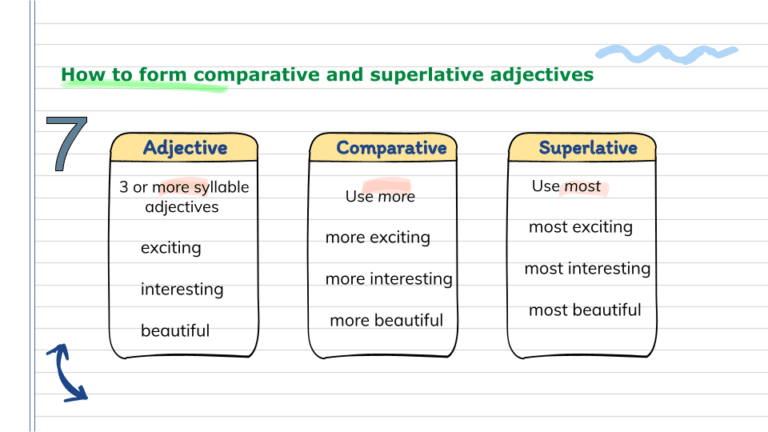
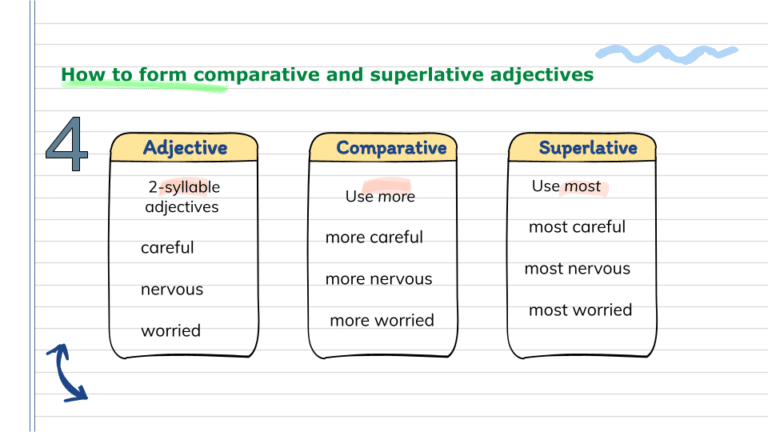
Adjectives with two or more syllables
Comparative: more + simple adjective + than
- He was more nervous than his wife when the accident happened. (nervous = 2 syllables)
- E-books are more popular than printed books these days. (popular = 3 syllables)
Superlative: the most + simple adjective + in / of
- I was the most worried person in the family. (worried = 2 syllables)
- Your painting is the most beautiful painting in the gallery. (beautiful = 4 syllables)
The comparative / superlative forms of some adjectives can be both with er / est or more / most. The most common of these are the following.
clever, common, cruel, friendly, gentle, narrow, pleasant, polite, shallow, simple, stupid, quiet
Spelling tips
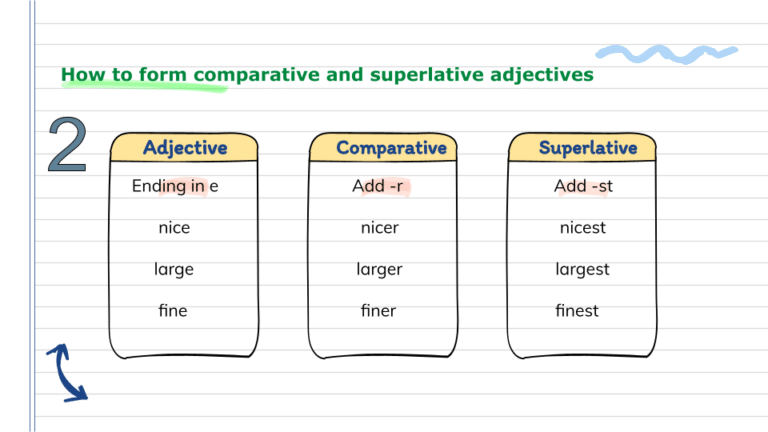
If the one-syllable adjective ends in e, we add r and st only.
- My new house is larger than my old house.
- This auditorium is the largest room in the school.
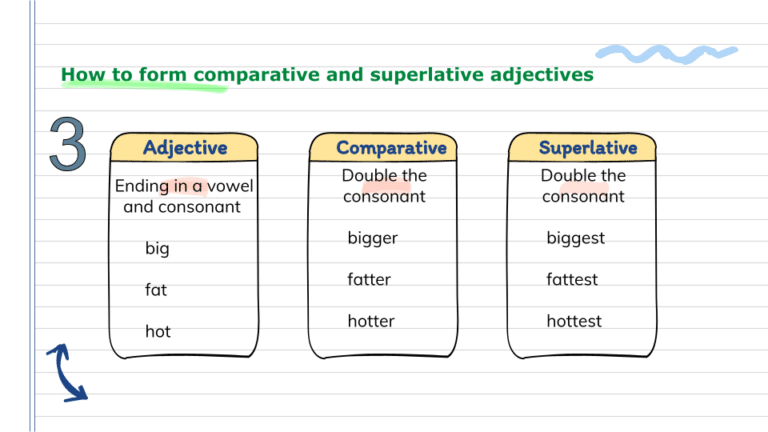
If the adjective ends in a stressed vowel and one consonant, we double the final consonant before we add the er or est.
- Summer in my city is hotter than summer here. (hot)
- It is the biggest city in the country. (big)
(Compare with strong – stronger – strongest, which ends in one vowel and 2 consonants.)
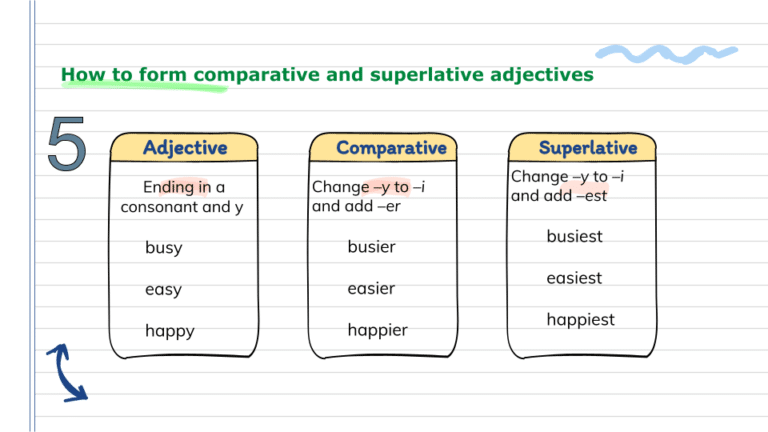
If the adjective ends in y, we remove the y and add ier or iest.
- This exercise is easier than the previous one. (easy)
- Your street is the busiest street in the city. (busy)
Irregular adjectives
These adjectives have comparative and superlative forms that do not follow the general rules listed above.
- good better the best
- well better the best
- bad worse the worst
- ill worse the worst
- much more the most
- many more the most
- a lot of more the most
- little less the least
- few less the least
- far farther the farthest (distance)
- far further the furthest (extent)
as + simple adjective + as
We use this structure if two people or things are similar.
To form the negative, we add not before the structure.
- Sami is as tall as his father.
- The green box is as heavy as the red one.
- The new house is not as big as the old one. (= The old house is bigger than the new one.)
Notes:
1. We can use much, a lot, and a bit before comparisons.
- The prices in this mall are very much higher than what they used to be a month ago.
- She is a bit older than her husband.
- This car is a lot more expensive than the one we saw yesterday.
2. After than, we can use either:
subject pronoun (I, you, we, they, she, he) + auxiliary (am, is, are, do, does, did, etc.)
OR
object pronoun (me, you, us, them, her, his).
- My brother is older than I am.
- My brother is older than me.
- She types faster than he does.
- She types faster than him.
A Common Mistake
Double comparative/superlative:
- My hair is more longer than hers. (Incorrect)
- My hair is longer than hers. (Correct)
- I have the most largest memory card. (Incorrect)
- I have the largest memory card. (Correct)